What is the purpose of the Ohio EPA Form 4309?
The Ohio EPA Form 4309, also known as Supplement to Form A – B1, is a comprehensive application used for the Permit-to-Install/Plan Approval process for sanitary sewers in Ohio. This form is vital for applicants seeking authorization from the Ohio Environmental Protection Agency's Division of Surface Water to construct or modify sanitary sewer systems. It collects detailed information about the project, including descriptions of the sewer system design, pipe specifications, flow calculations, design considerations for the receiving wastewater treatment facilities, and measures to protect water supplies and ecosystems.
Who needs to complete Ohio EPA Form 4309?
Any entity—be it a local government, private company, or individual—planning to install or modify a sanitary sewer system in the State of Ohio must complete the Form 4309 as part of their Permit-to-Install application. This requirement extends to projects involving new constructions, extensions, or alterations to existing sanitary sewers. Completing this form is a critical step in ensuring that the proposed sewer project meets the environmental and health standards set forth by the Ohio EPA.
Can future sanitary sewer extensions be added to the proposed project?
Yes, the possibility of future sanitary sewer extensions connecting to the new or modified system should be considered and mentioned in the application. Applicants are asked to discuss the potential for such extensions in the project description section of Form 4309. This foresight helps in planning for adequate capacity and environmental protection measures, ensuring that the sewer system can accommodate growth without compromising performance or violating environmental regulations.
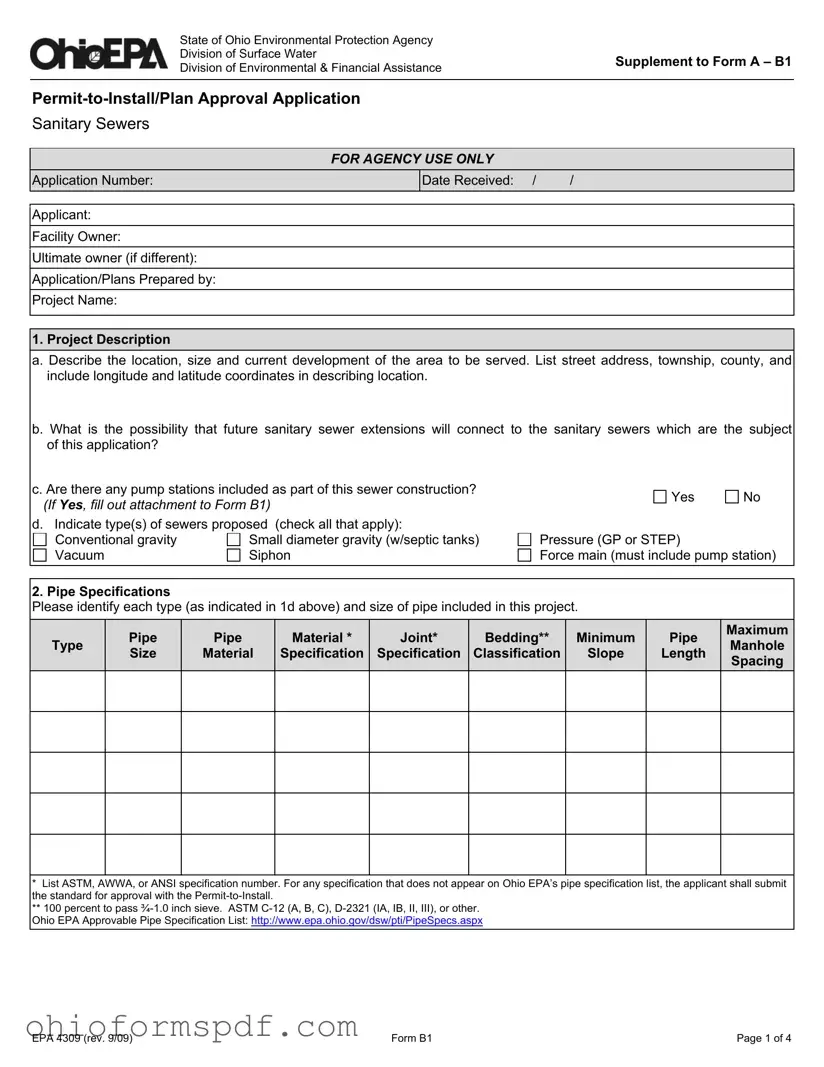
What information is required regarding pipe specifications?
Applicants must provide detailed specifications for each type and size of pipe included in the proposed sewer project. This includes the material of the pipes, joint and bedding classifications, minimum slope, pipe length, and maximum manhole spacing. Specifications must conform to standards acceptable to Ohio EPA, and any non-listed specification needs approval along with the permit application. This detailed information supports the evaluation of the project's design for durability, efficiency, and compliance with environmental standards.
How does the form address environmental and water supply protection?
Form 4309 includes sections focused on protecting streams, water supplies, and ensuring the design accommodates for environmental sustainability. Applicants must detail if the project involves stream crossings, proximity to public water systems, and measures to prevent sewer leakage, among other factors. These sections ensure that the proposed sewer installations do not adversely affect water bodies, comply with guidelines for minimizing ecosystem disruption, and safeguard against contamination of drinking water sources.
What are the testing and inspection requirements?
The form requires information on installation inspection, testing of sewer leakage, flexible pipe deflection testing, and manhole testing. Applicants must specify the type of tests that will be employed (e.g., hydrostatic, air testing) and identify the inspector. These requirements help ensure that the installed sewer systems are built to last, operate efficiently, and minimize risks of failures or environmental harm.
Is enforcement of sewer use ordinances addressed in the application?
Yes, applicants must affirm that ordinances or regulations prohibiting improper connections to the sanitary sewer system—such as roof drains and other clean water connections—are in place and enforced. This section of the application emphasizes the importance of maintaining the integrity of sanitary sewers and preventing overloading or contamination that could arise from unauthorized discharges into the system.



 No
No
 No
No
 No
No
 No
No
 No
No
 No
No
 No
No
