The Ohio IT-941 form, pertaining to monthly withholding information, shares similarities with the Ohio IT-942 form. Both serve as crucial elements in the process of reporting and remitting withheld taxes. The IT-941 form operates on a monthly basis, emphasizing periodic reporting, whereas the IT-942 is utilized for quarterly declarations. The common ground between these forms lies in their focus on ensuring accurate tax withholdings are reported and paid by employers, albeit on different schedules.
Similar to the Ohio IT-942 form, the Ohio SD-101 serves a specific purpose in withholding tax documentation, targeting school district withholding details. This form is specially designed for reporting taxes withheld on behalf of employees to local school districts. The simultaneous requirement for precision in recording withholdings connects the SD-101 closely with the IT-942, as both demand detailed financial information to comply with state and local tax regulations.
The process outlined in the Adding/Removing School Districts section is notably akin to the method described in the Ohio IT-942 for managing withholding account specifics. These segments guide users through adjustments in account details, be it for a school district or a general tax withholding purpose. Here, the essence lies in administrating tax-related data to maintain up-to-date records for compliance and accurate filing, showcasing the administrative parallels between managing school district information and quarterly tax withholdings.
The Ohio SD-141, like the IT-942, plays an integral role in facilitating tax administrative tasks. The SD-141 form is used for annual reconciliation of school district taxes withheld, analogous to the IT-942's function for quarterly tax reconciliation. Both documents necessitate a year-end or period-end review of tax amounts withheld versus amounts due, ensuring entities have appropriately met their taxation obligations.
The IT-942 4th Quarterly/Annual Reconciliation process bears resemblance to procedures found in other tax reconciliation practices, such as those for federal Form W-2 and W-3 reporting. This comparison arises from the need to reconcile and report the total amount of taxes withheld from employees with amounts actually remitted to the tax authority, serving as a check to ensure that withholdings are accurately reported and submitted for both state and federal taxes.
The Withholding Account Maintenance section in the IT-942 documentation resembles features found in general payroll software platforms. These systems offer functionalities for adding, updating, and deleting account information, mirroring the manual process detailed in the IT-942 guide. The core objective is managing business and employee information effectively to comply with tax withholding requirements, whether through automated software or manual entry.
The Billing Notice Payment instructions within the IT-942 documentation share similarities with procedures for managing notices and penalties in tax software or compliance systems. Such sections provide guidance on responding to specific tax notices, including payments for underreported taxes or penalties, drawing parallels in the handling of tax compliance issues across different platforms and forms.
Making Payments, as outlined in relation to the IT-942 form, is a fundamental task that aligns closely with functionalities seen in online tax payment systems used by federal and state tax authorities. The focus is on ensuring timely and accurate tax payments, a commonality shared across many tax-related documents and systems. This involves confirming the correct amounts are paid to the appropriate tax entity to avoid underpayment penalties.
The Assessment Payment segment contains instructions which can be likened to similar procedures in handling audits, assessments, or adjustments by tax authorities. Both in the context of the IT-942 form and broader tax practices, responding to assessments involves reviewing the tax authority's findings and remitting any additional amounts owed, ensuring tax compliance is maintained.
Finally, the concept of Payment Only submissions, as noted in the IT-942 documentation, is commonly encountered in direct tax payment arrangements across various tax forms and systems. This approach allows payers to make payments independent of regular filing schedules, commonly used for settling estimated taxes or addressing owed balances post-assessment, reflecting a flexible option for maintaining tax compliance.




 to display the
to display the  to display the
to display the  . The system saves the information and returns to the
. The system saves the information and returns to the 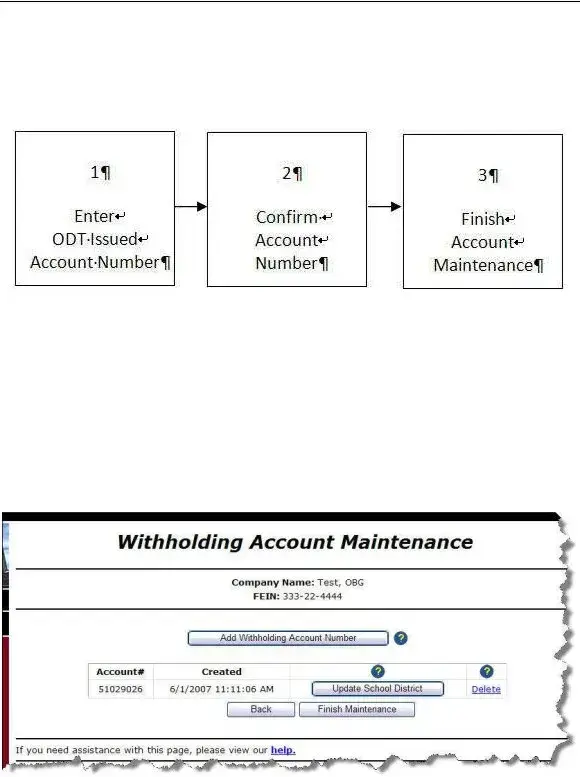

 . The system displays the
. The system displays the 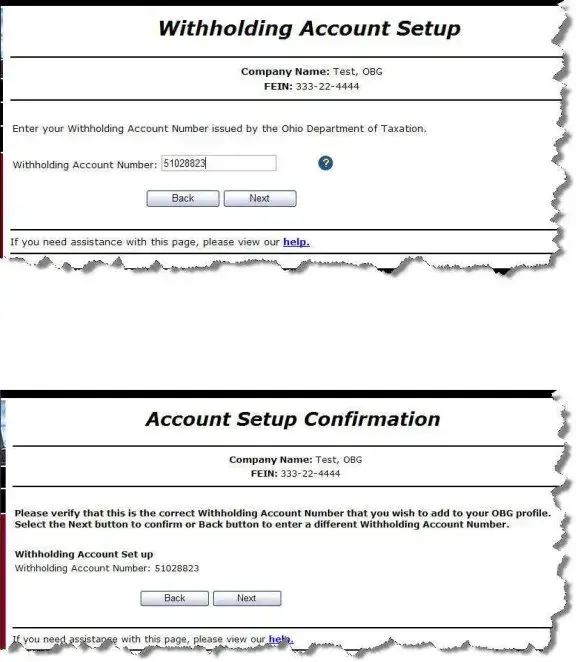
 . The system asks you to verify that you want to add this account number to your profile.
. The system asks you to verify that you want to add this account number to your profile. to verify that you want to add this account number to your profile. The system returns to the Withholding Account Maintenance page and displays the added account number in your list of profile accounts.
to verify that you want to add this account number to your profile. The system returns to the Withholding Account Maintenance page and displays the added account number in your list of profile accounts.
 to return to the
to return to the